VXLAN allows us to create layer 2 networks over layer 3 infrastructure. The VXLAN base use case is to connect two or more layer three network domains and make them look like a common layer two domain. In the Data center environment this allows virtual machines on different networks to communicate as if they were in the same layer 2 subnet.
VXLAN bridging is the concept of using the VXLAN protocol to provide layer 2 connectivity across the layer 3 infrastructure. VxLAN itself doesn’t have any control plane and rely on flood and learn mechanism similar to classic switches or VPLS services.
With the usage of EVPN, mac address information can be distributed with MP-iBGP updates. Using route reflectors at the Spine layer is recommended for the scalability. (Spine-Leaf Architecture is the baseline for the VxLAN-EVPN networks.)
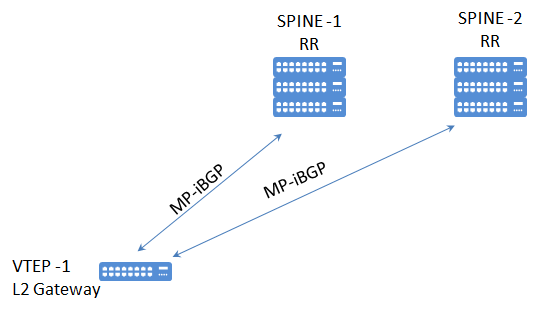
In this design, Leaf switches will only have MP-iBGP peering with both Spine switches. Spine switches will act as a Route Reflector and reflect the EVPN mac advertisements.
Let’s see the control and data plane step by step.
- We have Spine – Leaf topology with EVPN.
- 3 VMs in the same subnets are connected to 3 different Leafs.
- IP and MAC information of VMs and VTEPs are as below
- Route Distinguisher and Route Target both are 65000:1

- After VTEP-1 learns the mac address of VM1, with an ARP or any other type of packet sent by VM1, VTEP-1 will prepare and send following update to its peers. (It is configured to be peer with 2 Spines and Spines are route reflectors)
Type: MP_Reach_NLRI AFI:25 SAFI:70 Next Hop: 192.1.1.1 Route Type: Type 2 host advertisement route MAC Address: MAC-1 IP: 10.1.1.1 (optional) Route Distinguisher:65000:1 Route Target:65000:1 L2VNI: 29810
- Let’s assume, at the same time, VTEP-2 is also learned the mac address of its attached VM which is MAC-2 and advertised it to the its MP-iBGP peer as Type-2 route.
- Spine switches will reflect these updates to the other leafs because of route reflector configuration.
- VTEP -3 will get 2 different updates, including the one originated from VTEP -1 and one originated from VTEP-2
- VTEP -3 will have following entries in its EVPN forwarding table
MAC -1, 10.1.1.1, VNI:29810, Next Hop: 192.1.1.1 MAC -2, 10.1.1.2, VNI:29810, Next Hop: 192.1.1.2 MAC -3, 10.1.1.3, VNI:29810, Next Hop: local
- If the automatic tunnel creation option is used, VxLAN tunnel between VTEPs will be created automatically after the learning of remote VTEP ip address.
