Before Segment Routing was introduced, IP FRR and Loop-Free Alternates (LFAs) were not widely deployed. In these implementations the level of coverage depended on the network topology. When SR combined with FRR techniques, Fast Reroute can deliver 100% network coverage regardless of the topology. That is called TI-LFA (Topology Independent – Loop Free Alternate)
Here are some functions and benefits of TI-LFA;
- It is IGP automated. It is very simple to understand and deploy. No need to run and manage additional protocol.
- It can work and provide less than 50ms switch-over in any topology.
- TI-LFA finds and calculates the post-convergence shortest path to every possible destination.
- It can provide link protection, node protection and SRLG protection.
With TI-LFA, after the repair tunnel path is calculated and SID list is created, the SID list will be inserted into packet header. The insert behavior can different models according to incoming active segment.
If the incoming active Segment is Node SID/Prefix SID;

In that case, the Active Segment will be kept and repair path will be pushed. We assume link cost values are ok if node A2 pushes only the Node SID of Node A5.
If the incoming active Segment is Adj SID followed by another Adj-SID;
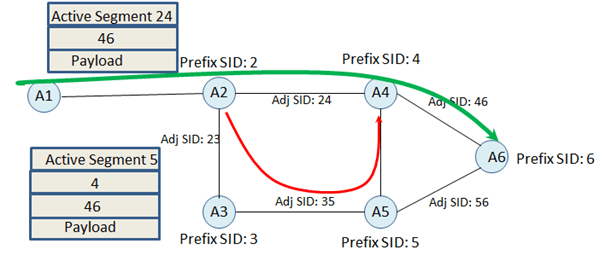
In this case Node A2 will do following operation;
– Next operation for Active SID
– Push Node SID of Adj
– Push Repair Path
If the incoming active Segment is Adj-SID followed by Node-SID;
In this case Node A2 will do following operation;
– Next operation for Active SID
– Push Node SID of Adj
– Push Repair Path
For the case where the active incoming segment is Adj-SID followed by a Node SID, there is also option not to push Node SID of peer, just find the new shortest path to the existing Node SID.
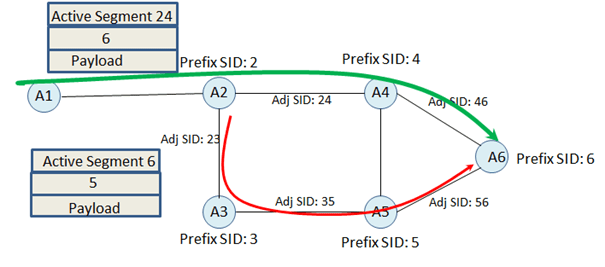
– Next operation for Active SID
– Push Repair Path
